Blockchain Solutions Beyond Crypto: Kenyan Use Cases
When people hear the word blockchain, many immediately think of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. But the truth is, blockchain technology is much bigger than crypto — it’s transforming how Kenyan industries operate. From agriculture to healthcare, logistics to education, blockchain is solving deep-rooted problems like data fraud, lack of transparency, and inefficient record-keeping.
In this article, we’ll explore how Kenyan businesses are adopting blockchain beyond crypto, what makes it revolutionary, and how E-Startups Kenya helps companies integrate blockchain solutions to achieve greater trust, speed, and security in operations.

Understanding Blockchain Beyond Crypto
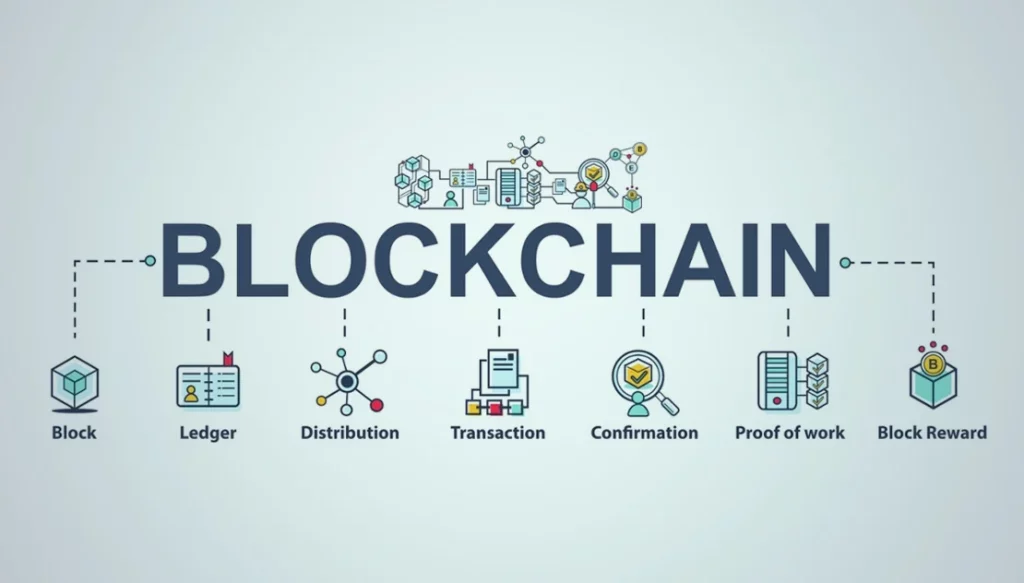
Blockchain is simply a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions securely across multiple computers. Unlike traditional systems where a central authority controls the data, blockchain allows participants to share, verify, and store records transparently.
For Kenya, where corruption, record tampering, and inefficiencies often hinder growth, blockchain offers a refreshing promise — trust without intermediaries. It’s like having a digital notary that no one can bribe, hack, or manipulate.

Why Blockchain Matters for Kenya
Kenya’s economy thrives on innovation. With initiatives like Konza Technopolis, Ajira Digital, and a booming fintech sector, blockchain fits perfectly into the country’s digital transformation vision.
According to a World Bank report (2023), adopting blockchain in Africa could save governments and companies up to $4 billion annually through reduced fraud, faster transactions, and improved transparency.
In Kenya, where mobile money and digital services are already part of daily life, blockchain applications are becoming increasingly practical.
I. Blockchain in Agriculture
Agriculture remains the backbone of Kenya’s economy, yet smallholder farmers often suffer from middlemen exploitation, counterfeit inputs, and delayed payments. Blockchain offers solutions by creating transparent supply chains.
For example:
Traceability: Farmers can record every stage of production — from seed to sale — ensuring authenticity and fair pricing.
Smart Contracts: Payments can be automated once a delivery is verified, ensuring farmers are paid instantly.
Input Verification: Blockchain verifies genuine seeds and fertilizers, preventing counterfeits.
Kenyan agritech startups like Twiga Foods and Farmshine are exploring such blockchain models to improve transparency and efficiency.

II. Blockchain in Healthcare
Kenya’s healthcare system faces challenges with patient data management, counterfeit drugs, and inefficient insurance processes. Blockchain brings order and trust to the system by ensuring secure, interoperable medical records.
Patient Data Portability: Hospitals can access patient records through encrypted, blockchain-based systems — reducing medical errors.
Pharmaceutical Supply Chain: Blockchain helps track medicine from manufacturer to pharmacy, preventing fake drugs from entering the market.
Insurance Claims: Smart contracts automate claim verification, reducing fraud and administrative delays.
Pilot projects by Kenyan innovators in collaboration with Amref Health Africa and IBM are already testing blockchain for medical record management.

III. Blockchain in Finance and Banking
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is reshaping Kenya’s fintech ecosystem by enabling faster, cheaper, and safer financial transactions.
Cross-Border Payments: Kenyan businesses trading with Uganda or Nigeria can use blockchain to transfer funds instantly, bypassing long banking processes.
Micro-Lending: Blockchain ensures lending transparency, recording every transaction to protect borrowers and lenders.
Asset Tokenization: Startups can tokenize assets like real estate or vehicles, allowing fractional ownership — opening investment to more Kenyans.
Financial institutions like Equity Bank and KCB Group are exploring blockchain-backed systems to improve transaction speed and security.
IV. Blockchain in Education
Kenya’s education system struggles with document verification — from fake certificates to lost academic records. Blockchain ensures every degree or transcript is verifiable and tamper-proof.
Credential Verification: Universities can issue blockchain-based digital certificates that employers can verify instantly.
Academic Records Management: Students’ academic journeys are stored permanently, reducing bureaucracy in transcript requests.
The Commission for University Education (CUE) has already discussed potential adoption of blockchain for academic certification to combat forgery.

V. Blockchain in Logistics and Supply Chain
Logistics companies in Kenya face challenges in tracking goods and verifying delivery. Blockchain provides real-time visibility and immutable records across transport chains.
Tracking and Verification: Every movement of goods can be logged and time-stamped, reducing loss or theft.
Paperless Trade: Blockchain automates customs documentation, reducing border delays.
Proof of Delivery: Smart contracts release payments only after confirmed delivery, ensuring accountability.
Firms like Sendy and Lori Systems are already leveraging data transparency, and blockchain could enhance these capabilities further.

How E-Startups Kenya is Empowering Businesses with Blockchain
At E-Startups Kenya, we go beyond buzzwords. Our focus is on real-world blockchain applications that drive efficiency, trust, and innovation.
We help businesses integrate blockchain into:
Supply Chain and Inventory Systems to improve product traceability.
Digital Identity Solutions for employees, vendors, or customers.
Smart Contract Automation to streamline operations and reduce costs.
Data Protection Frameworks that ensure compliance with privacy laws like Kenya’s Data Protection Act.
Whether you’re a fintech startup or an agribusiness enterprise, we design blockchain-powered systems tailored to your goals — secure, scalable, and user-friendly.

FAQs
1. Is blockchain only for big companies?
Not at all. Even small businesses can use blockchain for record-keeping, payments, and data protection. It’s scalable for any size.
2. Is blockchain expensive to implement in Kenya?
The cost depends on your project, but many blockchain solutions today are open-source and affordable for SMEs.
3. Can blockchain help prevent corruption in Kenya?
Yes. Because blockchain records are transparent and tamper-proof, they make it easier to track government and business transactions.
4. What industries benefit most from blockchain in Africa?
Agriculture, healthcare, education, and logistics are leading sectors, but fintech and energy are catching up fast.
5. How can E-Startups Kenya help my company use blockchain?
We design and implement blockchain systems customized to your operations — from supply chains to payment systems and digital identity management.
Conclusion
Blockchain is not just the future — it’s Kenya’s present. From farmers to fintech innovators, businesses are already proving that this technology can solve real African challenges. The shift beyond cryptocurrency is happening now, and those who adopt early will shape the next wave of digital transformation.
Ready to integrate blockchain into your business?
Reach out to E-Startups Kenya today. Let’s build transparent, data-driven, and future-ready systems that position your brand at the forefront of Africa’s digital revolution.